A New Grid Bridging System Tested at ACEP to Serve Villages in Alaska

Clockwise from bottom center: Alexander Radtke, Hannes Stuhring, Jeremy VanderMeer, Bill Thomson, Aimie Morgan, Tawna Morgan and Rob Cermak during blackstart testing of the inverter (starting the inverter to provide power after a system black out).
May 29, 2023
Testing has commenced on a new grid bridging system (GBS) at ACEP. A GBS is a short-term energy storage system that allows costly diesel generators to turn off for periods of time and to run on renewables to reduce fuel consumption. The 1-MW/1-MWh battery energy storage system will serve St. Mary’s and Mountain Village, two communities electrically connected via intertie on the Yukon River near the west coast of Alaska.
The GBS will be installed this summer in St. Mary’s. It will be used to provide spinning reserve to support integration of the 900-kW EWT wind turbine that was installed in St. Mary’s in 2018. The GBS will allow operation of smaller diesel generators and resulting fuel savings. The St. Mary’s GBS, manufactured by FREQCON, will be the first energy storage inverter deployed in Alaska that can connect into the power system without a transformer.
The GBS has been delivered to ACEP’s Energy Technology Facility (ETF) for comprehensive functionality and performance testing prior to shipping to St. Mary’s. Functional shakedown and initial acceptance testing commenced the week of April 24. Participating in the testing were Hannes Stuhring and Alexander Radtke, field personnel with FREQCON; Bill Thomson and Aimie Morgan from Alaska Village Electric Cooperative (AVEC), the electric power provider in St. Mary’s and Mountain Village; and Mariko Shirazi, David Light, Tawna Morgan, Rob Cermak and Jeremy VanderMeer from ACEP.
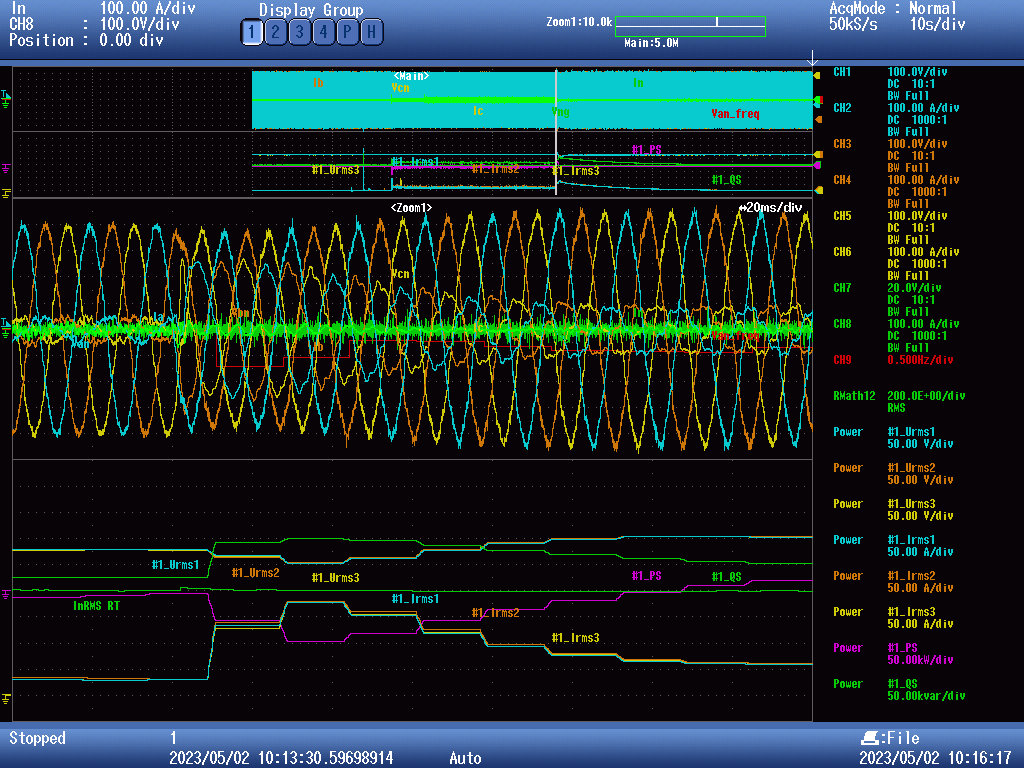
Current and voltage waveforms displayed on the oscilloscope screen during transition from grid-forming to grid-following operation.
The inverter was operated in both grid-following (GFL) and grid-forming (GFM) modes. A GFL inverter synchronizes and follows a “stiff grid” where the grid voltage is not significantly affected by system disturbances. A GFM inverter, on the other hand, is capable of generating a voltage waveform and providing power without requiring connection to an external grid. The St. Mary’s GBS will be operated in GFM mode.
The GFM operation was demonstrated both as stand-alone (inverter as the only source of power) and in parallel with the 320-kW and 400-kVA diesel generator at the ETF.
Full performance testing will commence in the upcoming weeks, so stay tuned!
This effort is a collaboration between ACEP, AVEC, and Sandia National Laboratory, and is being funded by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Electricity Energy Storage Division, DOE Office of Electricity Microgrid Program, and the Office of Naval Research.
For more information, please email Jeremy VanderMeer.


