Solar Photovoltaic Test Site

- Two monofacial and two bifacial modules mounted at a 60 degree tilt angle facing south.
- Two vertically oriented east-west facing bifacial modules
- All modules at the test site are grid connected through microinverters
- The test site is equipped to collect meteorological and power generation data one minute averages and all sensors are cleaned weekly.
- Additional details about the test site can be found in this peer-reviewed publication.
Irradiance instrumentation collects the following data:
- Albedo
- Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI)
- Global Normal Irradiance (GNI)
- Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI)
- Diffuse Horizontal Irradiance (DHI)
- Plane of array and rear plane of array irradiance measured with reference cells
Meteorological instrumentation:
- Ambient Temperature and Relative Humidity
- Wind Speed and Direction
- PV Module Temperature
- Rainfall
- Barometric Pressure
Designed for multiple PV module orientations, the solar test site on the University of Alaska Fairbanks campus, developed in partnership with Sandia National Laboratories in 2018, features bifacial panels and state-of-the-art meteorological and power monitoring equipment to measure ambient weather conditions as well as direct, diffuse, and global solar radiation. The data collected provides insight into the benefits of these and other emerging technologies in northern locations to inform the leading edge in solar technology.
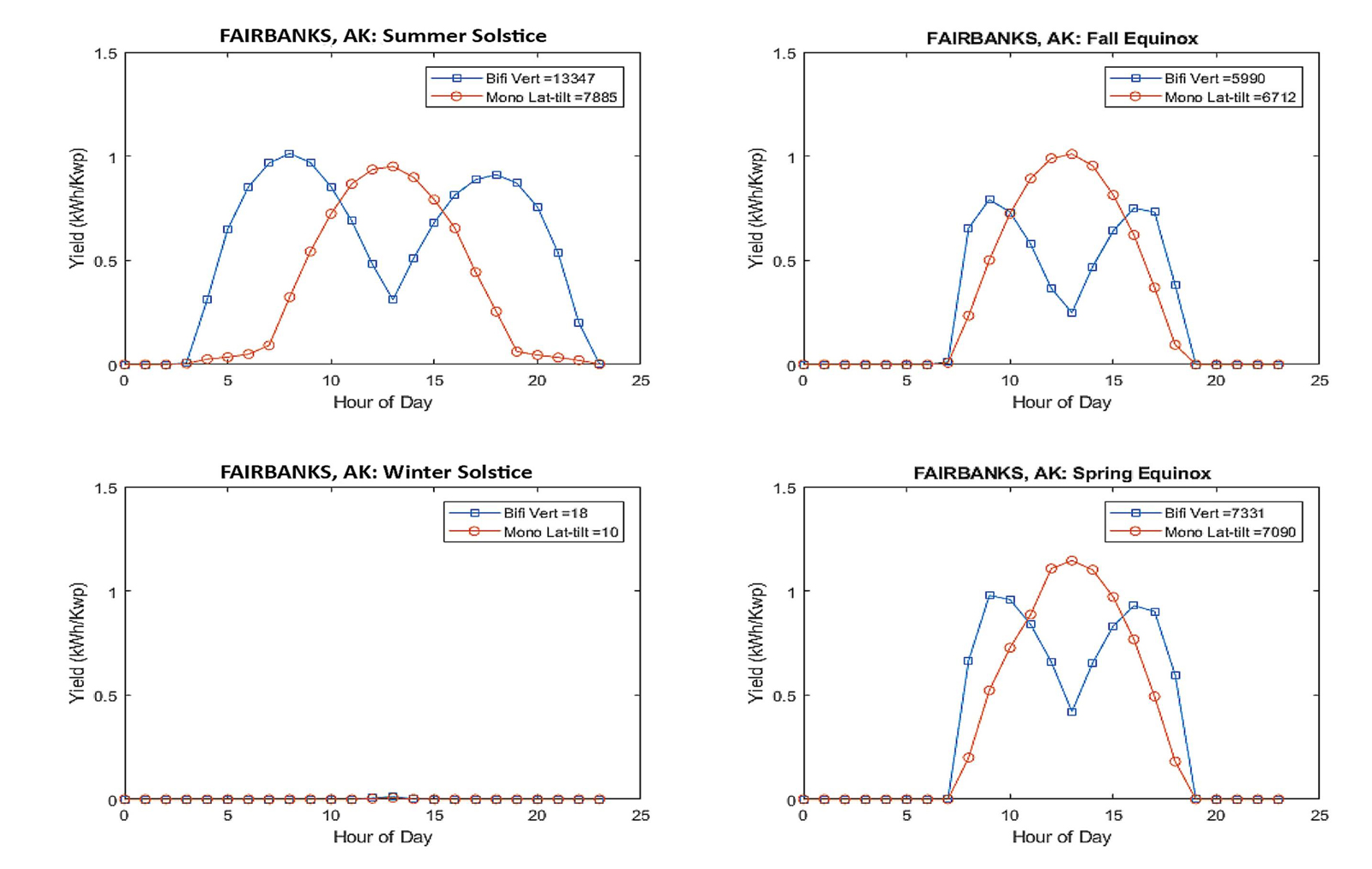
The Bifacial Advantage
In northern latitudes, vertically mounted bifacial panels facing east and west show enhanced output relative to traditional south-facing tilted monofacial panels. And due to the large solar azimuth at high latitudes, their production profile is also different.
Contact
Our Services
ACEP works with a diverse range of academic, industry, and community partners to meet the research needs of Alaska and beyond.


