Grid Bridging System Could Replace Diesel Generators in Microgrids
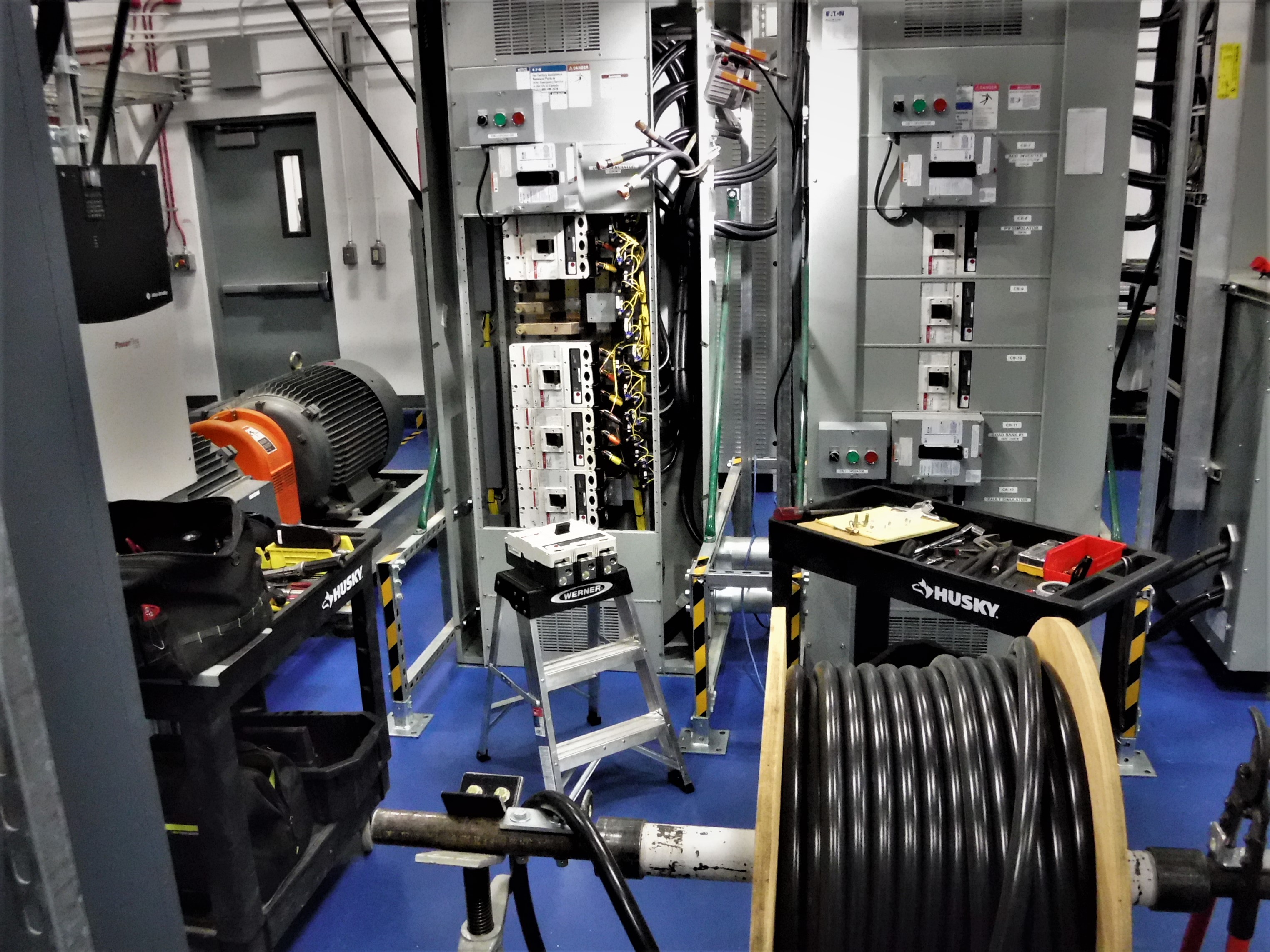
ACEP’s Energy Technology Facility is preparing to install a grid bridging system. This is an energy storage system designed specifically to provide the spinning-reserve and grid-forming services that are normally provided by diesel generators in microgrids, such as those in rural Alaska.
The very focused and intentional design of the GBS system will allow it to be integrated into diesel microgrids easier than many other energy storage systems and at a lower system cost.
The services from the GBS allow diesel generators to be turned off when there is sufficient renewable energy generation, maximizing the savings from the renewable energy. The GBS that ACEP will be testing uses a lithium iron phosphate battery as the energy storage technology. There are other energy storage technologies that we are monitoring that would be ideal for this application once they hit a low enough price point.
ACEP is partnering with the Alaska Village Electric Cooperative, and together they worked to specify the requirements for a GBS and identify appropriate technology. AVEC purchased the GBS. ACEP will test it in the lab before installing it in one of the AVEC communities to help integrate wind energy. ACEP also worked with Sandia National Laboratory to support the modeling and purchasing effort for the GBS.
Ultimately, the GBS will increase the savings that can be achieved from installing renewable energy into microgrids. The project is funded by Sandia National Laboratory and Office of Naval Research.
The grid bridging system is being installed in ACEP’s Energy Technology Facility. Photo by David Light.


