‘Remarkable groove’ slides gold into Alaska
March 6, 2020
Ned Rozell
907-474-7468

Nate Becker lives with his family on a quiet stretch of the Yukon River as it flows into Alaska. On a recent ski trip, I visited the Beckers’ home along with two geologist friends. Nate had a question for them.
“Why are all the gold deposits located on the south side of the river here, and none are on the north side?” Becker said.
A quick look at the map of Yukon-Charley Rivers National Preserve showed what Becker was talking about. In the 160 miles between the towns of Eagle and Circle, a half-dozen gold-mining settlements — most of them ghosted out — were on the south bank of the Yukon River. Not one was on the north side.
That seemed like more than a coincidence.
Bob Gillis, one of the skiers and a geologist who works for the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, said the gold imbalance was due to a slash in the Earth’s crust.
In 1904, R.G. McConnell of the Geological Survey of Canada named the Tintina Fault after an indigenous word for “chief.” The fault is a 1,000-mile line through mountains you can see on a zoomed-out map of eastern Alaska and western Canada. Over the centuries, earthquakes have hitched one part of the Earth’s crust past another as giant plates move. The Tintina Fault has maintained that channel between mountains.
The Tintina Fault hints at an answer to Becker’s question, Gillis said.
“When a mineral trend abruptly ends at a fault, sometimes the best thing to do is to look sideways,” he said. “In this case, the Yukon (territory).”
Over millions of years, the Tintina Fault has moved gold-bearing rocks from Canada into Interior Alaska. The Yukon River, as it enters Alaska, somewhat follows the trace of the Tintina Fault.
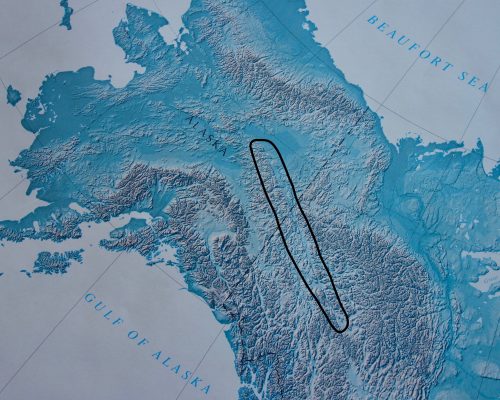
Like the San Andreas Fault in California, and the Denali Fault that tears a frown across the middle of Alaska, the Tintina Fault is a strike-slip fault with right-lateral motion. That means if you stand on one side of the fault — the weak part in Earth’s crust that might be a few miles wide — the landscape on the opposite side is moving to your right.
“To find the equivalent rocks underfoot on the other side of the fault, you’d have to step across it and walk to the right,” Gillis wrote. “For the Tintina, you’d need to pack a lunch.”
Geologists have found matching rocks on either side of the fault more than 200 miles apart. Gold deposit trends of Fairbanks, Circle and Livengood in middle Alaska are similar in age and style to those near Keno City in the Yukon territory.
The Tintina Fault slices through southern third of the Yukon territory. It then disappears for a bit before it connects with the Rocky Mountain Trench, a similar-but-longer feature that cleaves the high mountains in western Canada.
“The two trench-like valleys combine to form a remarkable groove ... from Montana to Alaska,” wrote geologist James Roddick in a 1967 paper.
So, to answer Nate Becker’s question, the Tintina Fault has delivered continental Canada gold to the south side of the Yukon River, but Canada has kept its own gold on the north side of the fault.
Since the late 1970s, the University of Alaska Fairbanks' Geophysical Institute has provided this column free in cooperation with the UAF research community. Ned Rozell is a science writer for the Geophysical Institute.


